When asbestos fibres are inhaled, they reside inside the body, causing a rare form of cancer called mesothelioma. Each year, around 800 Australians are diagnosed with mesothelioma, and around 750 people die from the terminal disease.
For this reason, it is imperative to avoid contact with asbestos. If you believe the harmful material is in your home, contact a licensed asbestos removalist.
In this blog article, we will discuss what mesothelioma is, how it affects the body, and how to avoid developing mesothelioma.
What is mesothelioma?
Mesothelioma is a cancer that affects the mesothelium. The mesothelium is a lining that covers most of the body’s internal organs, protecting them from rubbing against each other.
There are four main types of mesothelioma:
Malignant pleural mesothelioma
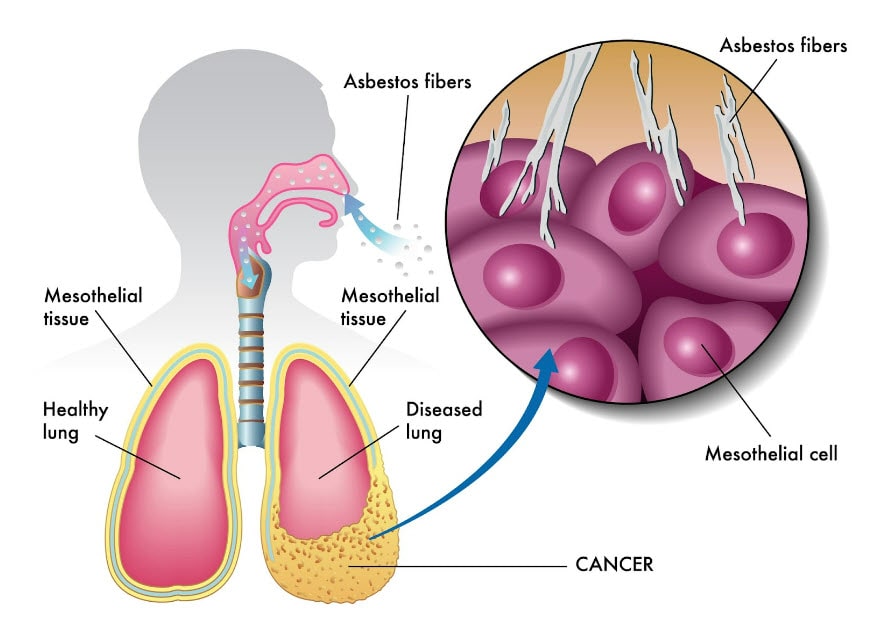
Malignant pleural mesothelioma is a type of cancer that forms in the lung lining and is the most common form of mesothelioma, accounting for around 70% of cases.
Malignant peritoneal mesothelioma
Malignant peritoneal mesothelioma affects the tissue around the abdomen. It accounts for around 20-25% of cases.
Malignant pericardial mesothelioma
Malignant pericardial mesothelioma is a rare form of mesothelioma that affects the tissue around the heart.
Malignant testicular mesothelioma
Malignant testicular mesothelioma is a very rare type of cancer that affects the lining of the testicles. Testicular mesothelioma makes up less than 1% of all mesothelioma cases.
What is the main cause of mesothelioma?
Mesothelioma is caused by exposure to asbestos. Asbestos is a group of minerals found in rocks and soil. They are made up of tiny fibres that can be released into the air and inhaled, which can then lodge themselves in the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart.
Most people who develop mesothelioma have worked in jobs where they were exposed to asbestos, such as construction work, shipbuilding, mining, insulation work, and firefighting. People exposed to asbestos through these kinds of jobs are at a much higher risk of developing mesothelioma.
However, it’s important to remember that mesothelioma can take many years to develop, so even if you were only exposed to asbestos a long time ago, you could still be at risk.
What are the symptoms of mesothelioma?
If someone is suffering from mesothelioma, they may experience a number of different symptoms.
These can include:
- Shortness of breath
- A persistent cough
- Chest pain
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
Mesothelioma can also cause other less common symptoms such as:
- Hoarseness
- Difficulty swallowing
- Fluid build-up around the lung (pleural effusion)
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to see your doctor so they can rule out other potential causes and provide you with the appropriate treatment.
What are the treatments for mesothelioma?
While there is no cure for mesothelioma, treatment options can extend a patient’s life and improve their quality of life.
After a mesothelioma diagnosis, treatment usually includes surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy. The best malignant mesothelioma treatment option will depend on its severity and your overall health.
How to prevent mesothelioma
The only way to prevent mesothelioma is by avoiding contact with asbestos. This can be difficult, as asbestos is found in many older residential and commercial buildings in WA, as it was legal to use the material until 2003.
If you believe your home or commercial building contains asbestos, don’t touch or try to remove it yourself. Any exposure to asbestos should be avoided as asbestos dust is deadly when inhaled.
Contact a certified asbestos removal contractor, so they can inspect the building and remove the asbestos.
Frequently asked questions
Malignant mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive disease that forms in the thin layer of cells lining the body's internal organs, known as the mesothelium. It is most commonly caused by exposure to asbestos. Symptoms of mesothelioma can include shortness of breath, chest pain, and a persistent cough, often with blood. There is no cure for mesothelioma, and treatment options are limited.
Mesothelioma isn't a type of lung cancer. Mesothelioma forms on the mesothelial lining, a membrane that protects several organs in the body. The mesothelial lining around the lung is the most commonly affected by mesothelioma. However, the cancer cells can form on the mesothelial lining protecting other organs, including the heart, abdomen, and genitals.
Any exposure to asbestos is dangerous. Even brief exposures can be deadly, and once the fibres are inhaled, they can't be expelled.
If you think you may have been exposed to asbestos, contact a doctor right away. Early diagnosis is essential for treatment options.
A mesothelioma prognosis depends on many factors:
- The stage of the disease
- The type of mesothelioma
- The patient's age and overall health
- Whether or not the disease has spread to other parts of the body
Mesothelioma tumours are growths that develop in the lining of the lungs, chest cavity, or abdomen. These tumours are usually caused by exposure to asbestos fibres, which can be very difficult to treat.
Symptoms of mesothelioma may not appear until many years after a person's initial exposure to asbestos, so it is important to be aware of the potential risks. If you have been exposed to asbestos, it is important to monitor your health closely and seek medical help if you develop any symptoms related to mesothelioma.
There is no one answer to this question as the latency period for asbestos-related diseases can vary depending on several factors, including the type of disease, the individual's exposure history, and other health conditions.
However, it is generally accepted that most asbestos-related diseases develop after many years of exposure to asbestos fibres. For example, mesothelioma, a cancer of the lining of the lungs, typically takes 20-40 years to develop following exposure. Therefore, if you have been exposed to asbestos at any point in your life, it is important to be aware of the potential health risks and closely monitor your health.
To diagnose mesothelioma, a pathologist will conduct a biopsy. This involves taking a small sample of tissue from the affected area and examining it for affected cells under a microscope. The pathologist will look for specific abnormalities that are characteristic of mesothelioma cells.


